Through small incisions, a camera and instruments are introduced and manipulated into the joint cavity.
A circulation of physiological fluid is established and maintained throughout the intervention, so as to guarantee optimal vision on a video screen.
Here is the kind of image that is obtained during a knee arthroscopy:

^ articular facet of the patella, with in the background a cannula which serves to evacuate the rinsing liquid.

^ above, the femoral part of the joint, covered with intact cartilage ; below, the cartilaginous surface of the tibia, also in good condition; in the middle, the meniscus, which has a tear.

^ Degenerative lateral meniscus, with at bottom the tendon of the popliteal muscle running through the joint.
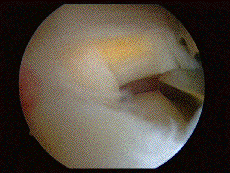
^ meniscus undergoing partial resection, with a degenerative part (in yellow).
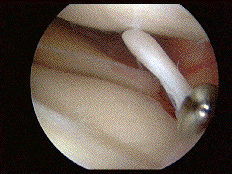
^ torn meniscus tab pulled apart by a hook.
What are the knee operations that can be performed by arthroscopy?
-
meniscus surgery
-
anterior cruciate ligament plasty
-
intervention on the cartilage (smoothing, grafting, etc.)
-
removal of "joint mice"
-
synovectomy for rheumatoid or inflammatory arthritis
The duration and nature of postoperative rehabilitation vary according to the type of operation; for the meniscus, the patient can get up immediately after the operation and walk fully weight-bearing, using crutches for a week; there is no need for a splint or cast. For operations on the cruciate ligaments and cartilage, rehabilitation is longer and more complicated.



